IoT AI and the future of connected devices
Explore the future of AIoT, where artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things converge to create smarter, autonomous devices across industries.
Ready to build your IoT product?
Create your Particle account and get access to:
- Discounted IoT devices
- Device management console
- Developer guides and resources
IoT AI and the future of connected devices
Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) represents the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling smarter, more autonomous connected devices. AI enhances IoT by allowing devices to perceive, learn, reason, and make decisions, unlocking new possibilities across various industries. Recent advancements have made AIoT more accessible than ever before:
- Sensor technology: Accelerometers, for example, have become cheaper due to their widespread use in cell phones, making them more affordable for various applications.
- Connectivity solutions: The progress in 5G, LPWAN, and Wi-Fi 6 technologies has improved available bandwidth and power efficiency.
- Edge computing and AI chips: Innovations in low-power compute have changed the landscape, enabling battery-powered devices to use AI.
- Data analytics and machine learning platforms: Developments in these areas have made it easier to process and analyze the vast amounts of data generated by IoT devices.
Understanding the fundamentals of AI and IoT
IoT refers to the network of physical devices and systems connected to the internet, enabling them to collect and exchange data. The key components of IoT include sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interfaces, all working together to generate valuable insights. With millions of connected devices already in the field and the number growing rapidly, the scale of IoT is crucial in driving AI development through massive amounts of data.
AI, on the other hand, is a branch of computer science that focuses on creating intelligent machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI encompasses various subsets, such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. In the context of IoT, AI enables devices to perceive, learn, reason, and make decisions, leading to more efficient and intelligent systems.
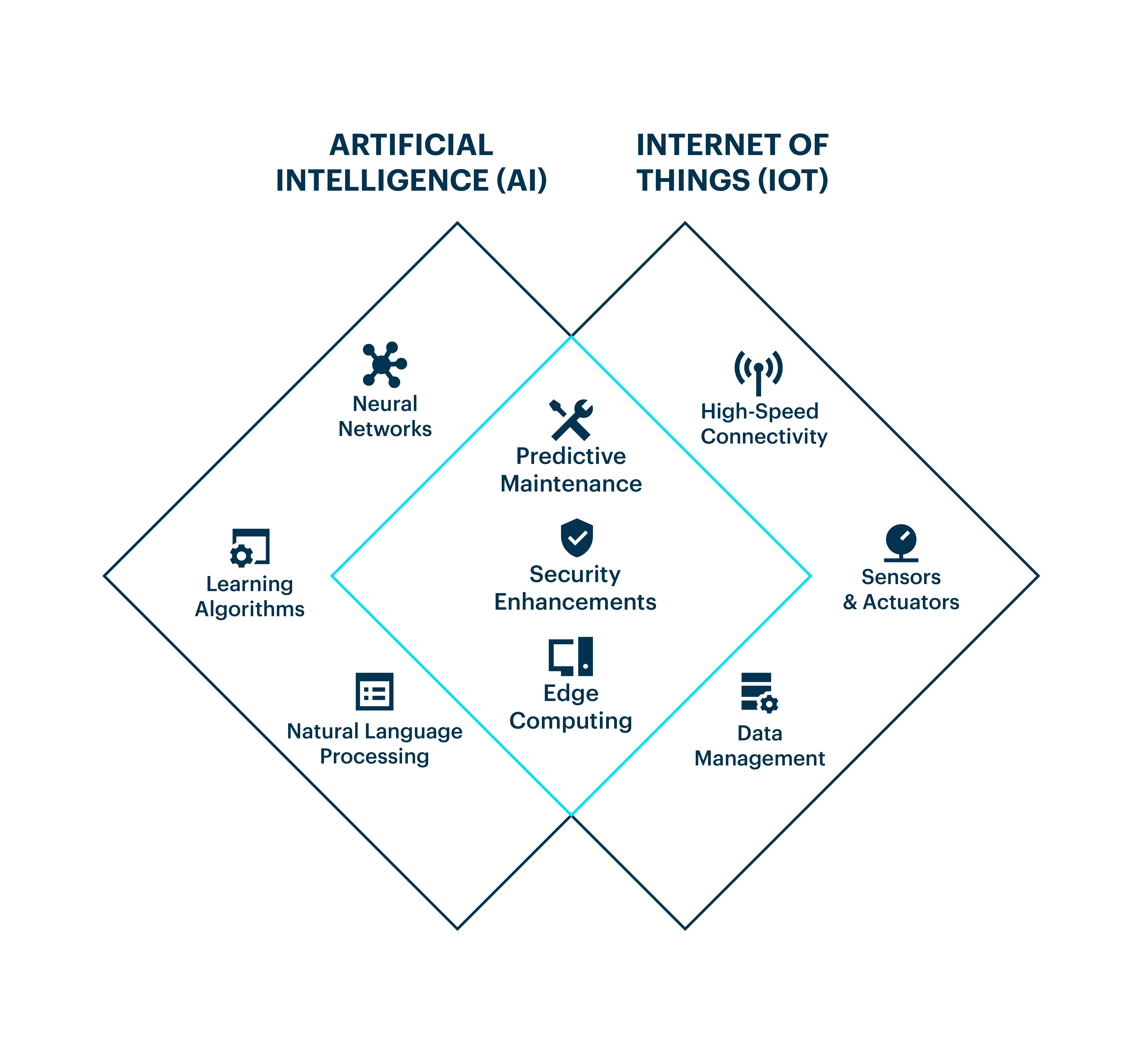
The AIoT architecture: Cloud-based and edge-based approaches
IoT artificial intelligence architectures can be divided into two main categories: cloud-based and edge-based.
| Approach | Layers | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud-based | Device, connectivity, cloud, user communication | Scalability, flexibility | Latency, data privacy |
| Edge-based | Edge, connectivity, cloud | Real-time insights, Reduced latency | Resource constraints |
Cloud-based AIoT leverages cloud computing for data storage, processing, and analytics, consisting of four layers: device, connectivity, cloud, and user communication. This approach offers scalability and flexibility but may face challenges related to latency and data privacy.
Whereas edge-based AIoT processes data closer to the source, enabling real-time insights and reduced latency. The three layers of edge-based AIoT are edge, connectivity, and cloud. As an infrastructure company, Particle focuses on providing robust solutions for edge-based AIoT deployments, empowering devices to make intelligent decisions without relying solely on cloud connectivity.
Data management and governance in Internet of Things AI
Effective data management is crucial for unlocking the full potential of AIoT. Best practices for data quality, integration, and governance ensure that the data collected by IoT devices is accurate, reliable, and secure. For artificial intelligence with IoT systems, scale plays a significant role in data collection, as vast amounts of data are necessary to drive meaningful insights. Governance is less of an issue in AIoT compared to other AI applications, as the data used in these systems is typically owned by the company building the AI.
Challenges and considerations for AIoT implementation
One of the key challenges in AIoT implementation is the choice between performing AI at the edge or in the cloud. Edge AI offers advantages such as real-time decision-making, reduced latency, and offline functionality, but it requires significant data collection to train the AI models before they can be miniaturized and deployed on resource-constrained devices. Conversely, cloud AI allows for more complex models but relies on high-bandwidth connectivity and raises concerns about data privacy and security.
Another crucial consideration is knowing what insights to look for in the data. AI is not a magic solution that can extract meaningful insights from any dataset; it requires domain expertise and a clear understanding of what the data can reasonably reveal. A conservative, incremental approach is recommended, focusing on the most important insights first and gradually expanding the scope of the AI system. It is essential to disconnect the hype from reality and recognize that AI is ultimately based on mathematical models and algorithms, not magical thinking.
Future trends and opportunities in AIoT
As AIoT continues to evolve, several trends and opportunities are emerging:
- Edge AI: Becoming increasingly important, implementing decentralized, on-device intelligence for real-time decision-making.
- 5G networks: Promising to unleash new possibilities with ultra-low latency and high bandwidth connectivity.
- AIoT for sustainability: Enabling energy efficiency and environmental monitoring.
- Particle's focus on infrastructure: Supporting massive data collection through new connection technologies like non-terrestrial networks (NTN).
- Smart infrastructure: Representing a significant opportunity for AIoT to drive innovation and efficiency in urban environments.
Embracing the AIoT revolution
AIoT represents a transformative force that combines the power of AI with the scale and reach of IoT. By enabling smarter, more autonomous connected devices, AIoT has the potential to revolutionize industries and drive unprecedented levels of innovation and efficiency. As technology leaders explore the possibilities of AIoT, it is crucial to address the challenges associated with data management, scalability, and ethical considerations.
Particle's Tachyon represents a significant step forward in AIoT technology. As a 5G-connected single-board computer with a powerful Snapdragon SoC and AI accelerator, Tachyon offers the processing power and connectivity needed for advanced edge-based AIoT applications. Its versatility makes it an ideal platform for developing and deploying innovative AIoT solutions across various industries.
To learn more about Tachyon and how it can power your AIoT applications, visit Particle's website or talk to our sales team.