The 2024 guide to IoT sensors
Learn how IoT sensors enhance smart systems through real-time monitoring, automation, and environmental control across various applications.
Ready to build your IoT product?
Create your Particle account and get access to:
- Discounted IoT devices
- Device management console
- Developer guides and resources
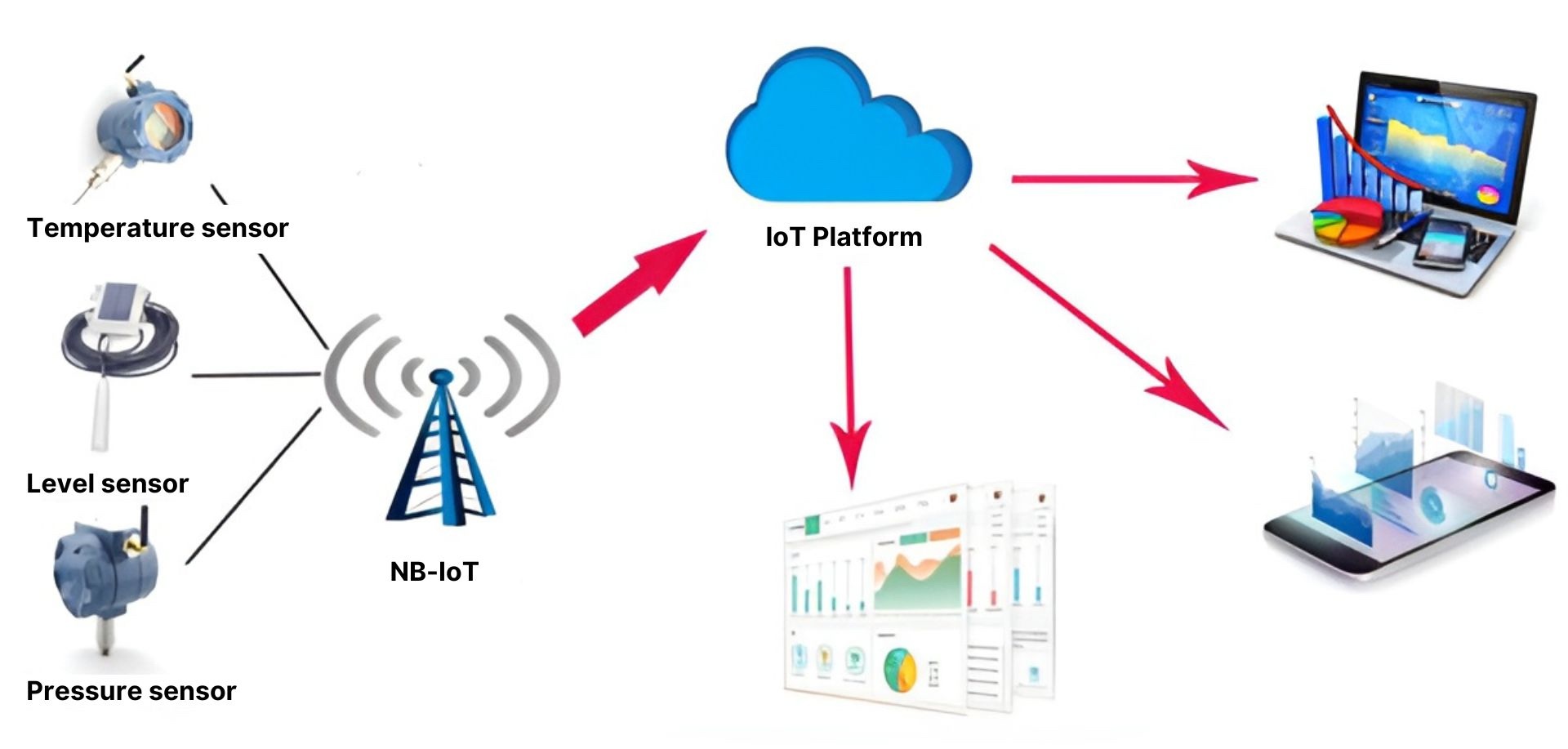
Unlocking the full potential of IoT starts with understanding its core components: sensors – the eyes and ears of smart systems. These essential sensor devices collect and transmit data about the physical environment, enabling smart systems to make informed decisions and automate actions. This guide explores the various types of IoT sensors and their applications, offering a detailed look at the building blocks of IoT technology.
What are IoT sensors?
IoT sensors are devices that detect and measure physical properties or changes in the environment, converting this information into digital data. These small, often energy-efficient devices can be embedded into various objects or environments, acting as the bridge between the physical and digital worlds.
When connected to a network, these sensor devices transmit their data to cloud-based platforms or local systems for analysis and action, enabling real-time monitoring, automated decision-making, and intelligent responses to changing conditions without human intervention.
Sensors for IoT come in many forms, each designed to capture specific types of data such as temperature, motion, light, or sound. Their applications span across various industries and aspects of daily life, from enhancing home automation to optimizing industrial processes. In the following sections, we'll explore some of the most important types of IoT sensors you should know about.
Environmental sensors
Temperature sensors
What they are: Temperature sensors measure the thermal energy of a substance or environment, converting it into an electrical signal for measurement and monitoring purposes.
How they're used: Temperature sensors enable real-time temperature tracking across various environments, facilitating automated adjustments in heating and cooling systems. They support energy optimization, equipment protection, and climate control by continuously transmitting temperature data to connected systems.
Common applications: Smart HVAC systems, industrial equipment monitoring, cold chain management, and environmental studies.
Humidity sensors
What they are: Humidity sensors detect and measure the amount of water vapor present in the air or other gases.
How they're used: Humidity sensors help maintain optimal moisture levels in sensitive environments. They allow automated control systems to make precise adjustments based on continuous humidity data, ensuring energy efficiency and product quality in various settings.
Common applications: Climate control systems in museums and data centers, industrial processes, agricultural management, and conservation of sensitive materials.
Pressure sensors
What they are: Pressure sensors measure the force exerted by liquids or gases on a surface, typically converting this force into an electrical signal.
How they're used: These sensors provide valuable data for monitoring and controlling fluid and gas-based processes. They enable rapid response to pressure changes and anomalies, supporting system integrity and safety protocols in various industries and applications.
Common applications: Industrial process control, smart city water management, vehicle tire pressure systems, and weather monitoring stations.
Light sensors
What they are: Light sensors, also known as photodetectors, measure the intensity of light in the environment and convert it into an electrical signal.
How they're used: Light sensors enable real-time monitoring of ambient light conditions, facilitating automated adjustments in lighting systems. By providing accurate light intensity data, they support energy conservation efforts and adaptive lighting solutions.
Common applications: Smart lighting systems, agricultural monitoring for optimal plant growth, display technologies, and automated shading systems in buildings.
Gas sensors
What they are: Gas sensors detect and measure the concentration of specific gases in the environment, converting the chemical interaction with gases into electrical signals.
How they're used: Gas sensors enable real-time detection and measurement of various gases, facilitating rapid response to potential hazards or environmental changes. They support safety protocols, environmental management, and process control by providing accurate gas concentration data.
Common applications: Air quality monitoring, industrial safety systems, smart home safety features, and emissions tracking.
Motion and position sensors
Accelerometers
What they are: Accelerometers measure the rate of change of velocity of an object, detecting movement and orientation changes.
How they're used: Accelerometers provide motion and orientation data, enabling real-time movement tracking and analysis. They facilitate automated responses to changes in motion or position, supporting various functions from user interface control to equipment monitoring.
Common applications: Wearable devices, smartphone controls, industrial machinery monitoring, and vehicle stability systems.
Gyroscopes
What they are: Gyroscopes measure angular velocity, providing data about an object's orientation and rotational movement.
How they're used: Gyroscopes work alongside accelerometers to provide precise motion and orientation data. They enable accurate tracking of rotational movements, facilitating navigation and stabilization in various systems, from handheld devices to large machinery.
Common applications: Navigation systems, drone stabilization, virtual reality devices, and robotics.
Proximity sensors
What they are: Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of nearby objects without physical contact, using various technologies such as infrared, capacitive, or ultrasonic sensing.
How they're used: These sensors enable non-contact detection and measurement, supporting various automation and safety applications. They provide real-time data about the presence and distance of objects, facilitating automated responses in smart environments. __ Common applications__: Automated doors, touchless interfaces, obstacle detection in autonomous systems, and occupancy monitoring in smart buildings.
Ultrasonic sensors
What they are: Ultrasonic sensors emit high-frequency sound waves and measure the time it takes for the waves to bounce back, calculating the distance to objects.
How they're used: Ultrasonic sensors provide accurate distance measurements for various monitoring and control systems. They enable precise object detection and ranging in diverse environments, supporting functions from basic presence detection to complex spatial mapping.
Common applications: Parking assistance systems, liquid level monitoring, robotic navigation, and industrial automation.
Electromagnetic sensors
Current and voltage sensors
What they are: Current sensors measure the flow of electric current in a circuit, while voltage sensors detect the electric potential difference between two points.
How they're used: Current and voltage sensors are fundamental to energy management and electrical safety. They enable monitoring of power consumption and distribution, facilitating efficient load balancing and fault detection in electrical systems.
Common applications: Smart grids, energy management in buildings, electric vehicle charging systems, industrial equipment monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
Magnetometers
What they are: Magnetometers measure the strength and direction of magnetic fields in their vicinity.
How they're used: Magnetometers enhance spatial awareness and detection capabilities in various devices. They provide data on magnetic fields, enabling devices to interact more intelligently with their environment and supporting navigation and detection functions.
Common applications: Digital compasses in smartphones, vehicle detection in parking systems, non-destructive testing in industry, and security systems.
Acoustic sensors
Sound sensors (microphones)
What they are: Sound sensors, or microphones, convert acoustic waves into electrical signals, capturing audio information from the environment.
How they're used: Sound sensors capture and analyze audio data, enabling a wide range of audio-based applications. They enhance user interfaces, improve environmental monitoring, and enable more intuitive and responsive systems across multiple sectors.
Common applications: Voice-activated smart home assistants, noise pollution monitoring in smart cities, predictive maintenance in industry, and patient monitoring in healthcare.
Vibration sensors
What they are: Vibration sensors detect mechanical oscillations in structures or machinery, converting them into electrical signals.
How they're used: These sensors detect mechanical oscillations, playing a crucial role in structural and mechanical health monitoring. They enable predictive maintenance by detecting unusual vibrations, helping prevent breakdowns, and optimizing performance in various settings.
Common applications: Industrial machinery monitoring, structural health assessment in smart buildings, condition monitoring of transportation infrastructure, and seismic activity detection.
Getting started with IoT sensors
IoT sensors are the foundation of smart systems, collecting crucial data from our environment. As technology advances, sensors will become smaller, more energy-efficient, and capable of processing more complex data, enabling increasingly sophisticated IoT applications across industries.
If you're interested in exploring IoT sensor integration, consider starting with Photon 2 Wi-Fi board or the Boron LTE-M with EtherSim along with the Grove Starter Kit, which includes a variety of sensors that allow you to experiment with different IoT applications. This hands-on approach can help you understand how sensors work within IoT systems and spark ideas for your own projects.